__________________________________________________________________________________
GREECE – Axios Delta National Park, Kalochori Delta
__________________________________________________________________________________
The Greek case study covers an area of 762 km2. It concerns the coastal area of Thermaikos Gulf and includes part of the city of Thessaloniki and the Axios Delta National Park (Axios National Park – Loudias river – Aliakmonas river).
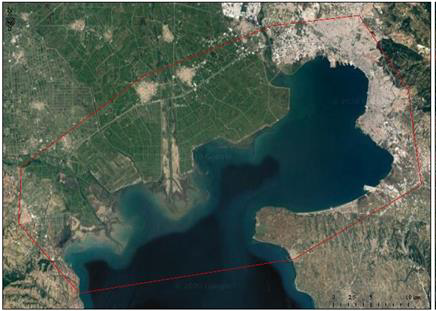
The high environmental importance of the area is evident from the fact that, in 1975, the region of the Axios-Loudias-Aliakmonas Delta was included in the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance. Additionally, since 1996, it has been integrated in the European Network of Protected Area Natura 2000, while four areas, under the responsibility of the Axios Delta National Park, have been characterized as Wildlife Refuges which main objective is the protection and development of biotopes
Furthermore, this region is a coastal area close to a river delta and combines, not only a plethora of land uses (urban, industrial, commercial zone), but also, a variety of economic activities, which in many cases are in conflict with environmental protection and have significant environmental impacts.
Due to all these reasons, Kalochori Delta is an optimal choice for the Greek case study under the EPIPELAGIC project which will provide valuable knowledge for investigating the related physical mechanisms.
__________________________________________________________________________________
CHINA – Yellow River Delta
__________________________________________________________________________________
The Chinese case study covers the coastal area of the Yellow River Delta, at least 10,000 km2, located in the Xianhe Town, Dongying City and Shandong Province
This region is an important industrial zone for China due to oil and gas exploration, salt production, aquaculture, etc. The Gudong Oilfield, which is located in the northern delta region of the Yellow River, is part of China’s second largest oilfield, the Shengli Oilfield. Gudong coastal dam was built in the 1980s to prevent the intrusion of seawater and provide the only protection of the oilfield. Its length is 12 km, and represents the most important security barrier between the Gudong Oilfield and the Bohai Sea.
Due to its special geological environment, the over-exploitation of its underground resources and the increasing human activity, the oilfield and its affiliated facilities are vulnerable to the threat of land deformation. At the same time, rising sea-levels caused by climate change results to an increase in the frequency of marine disasters
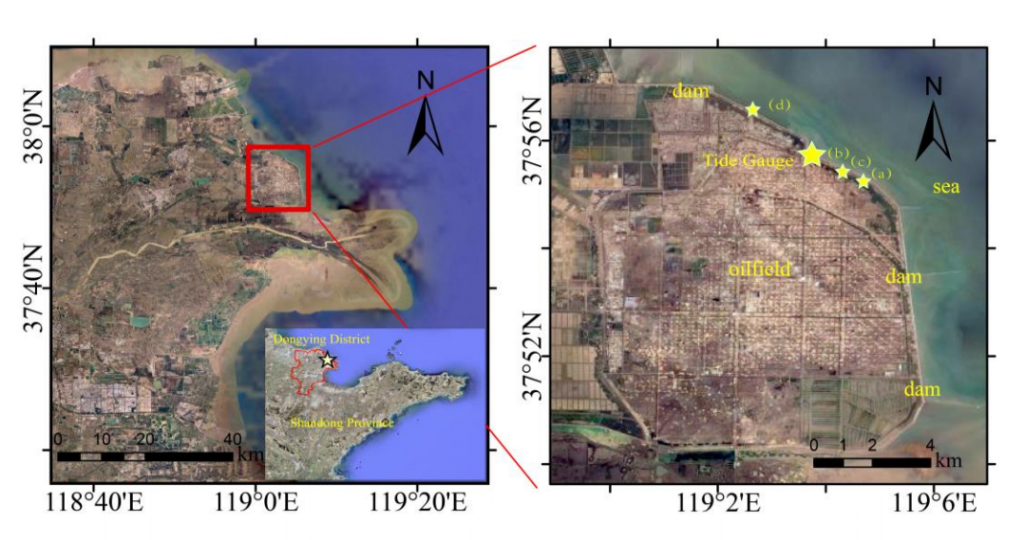
Therefore, it is of great importance to monitor the region of the Yellow River Delta for the Chinese case study under the EPIPELAGIC project and contribute to risk mitigation and new planning policies.

